Principle:
Osmosis
is a natural process that when a pure water and saline water are separated by a
membrane which can permit only water molecules to pass through. Pure water will
flow into the saline water due to a tendency called osmosis. This natural
tendency can be reversed by applying an opposite pressure to the saline water
so that water molecules from saline water tend flow out as pure water. This is
called reverse osmosis.
Process:
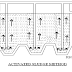
·
It consists of several horizontal
compartments separated by semi-permeable membranes.
·
A
pressure of 15-40 kg/cm2 is applied to the saline water to force its
pure water to pass through the semi-permeable membrane leaving behind the
dissolved salts.
·
The pure water from different compartments
are collected and the concentrated saline water left out is discarded.
·
The membrane is generally a thin film of
cellulose acetate or polymethyl methacrylate.
Advantages:
1.
This method is economical, compact and very simple.
2.
Life time of the membrane is high about 2 years.
3.
Easy to replace the membrane within two minutes.
4.
Ionic, non ionic, colloidal and high molecular weight organic matters are
easily removed.